Chlamydia Treatment
Chlamydia is an STI (Sexually Transmitted Infection) caused by the spread of bacteria, known as Chlamydia Trachomatis. It is spread when an infected person engages in sexual activity with a non-infected person. If left untreated, chlamydia can cause long term complications such as infertility and reactive arthritis (pain and swelling in your joints).
CHLAMYDIA TREATMENT
Chlamydia Treatment
Buy chlamydia antibiotics online after completing a short online consultation. No doctors visit required.
About Chlamydia
Chlamydia is caused by the spread of bacteria, known as Chlamydia Trachomatis. It is transmitted when an infected person engages in sexual activity with a non-infected person. If left untreated, chlamydia can cause long term complications such as infertility and reactive arthritis (pain and swelling in your joints).
The good news is that is it curable without the need to visit a doctor and the success rate of chlamydia treatments is high. The first line of treatment is doxycycline, it is more effective and less prone to antibiotic resistance. For those that cannot take doxycycline, the recommended alternative is azithromycin.
What causes chlamydia?
You can only get chlamydia by having unprotected sex with an infected person, or by coming into contact with semen or vaginal fluid of an infected person.
You can get chlamydia by:
- Unprotected sex (including vaginal, anal, and oral)
- Using sex toys that haven’t been washed after use or protected with a condom before use by an infected person
- Your genitals coming into contact with an infected person’s genitals, even if there is no penetration or ejaculation.
- Getting infected genital fluids (vaginal fluid or semen) in your eyes
(Read our blog to find out more about: Eye chlaymdia)
You cannot get chlamydia from:
- Kissing, hugging or sharing a bed with an infected individual
- Toilet seats or swimming pools
Chlamydia symptoms
Most of the time, chlamydia has no symptoms. Therefore, it is important to get yourself tested on a regular basis, especially if you have numerous sexual partners. In those that experience symptoms of chlamydia, they usually appear several weeks after contracting the infection. For some, they may not develop until many months later.
Symptoms of chlamydia in men:
- Pain or burning sensation whilst urinating
- Discharge from the penis - white, yellow or greenish in colour
- Pain and swelling in the testicles
- Discharge, bleeding or pain in the bottom
- Sore throat (oral chlamydia)
Read our blog to find out more about: Chlamydia symptoms in men
Symptoms of chlamydia in women:
- Pain during sex
- Abnormal vaginal discharge - milky white or yellow in colour and may have a strong smell
- Burning sensation or pain when peeing
- Tummy or pelvic pain
- Pain or discomfort during sex
- Bleeding after sex or bleeding between periods
- Discharge, bleeding or pain in the bottom
- Sore throat (oral chlamydia)
Read our blog to find out more about: Chlamydia symptoms in women
Not everyone gets symptoms
It is important to remember that chlamydia symptoms are not always present, and you should get tested regularly, especially if you have multiple sexual partners. At least 70% of women and at least half of all men with chlamydia don't notice any symptoms.
How to test for chlamydia
To test for chlamydia, you will be required to provide a urine sample, which is analyse in a lab. You can get a free chlamydia test on the NHS by going to a gum clinic or you can order a home chlamydia test kit, involving sending off a urine sample to the lab by post.
How long does it take for chlamydia to show up on a test?
Test results will normally be available in 7 to 10 days. If the likelihood of having chlamydia is high, for example if you have symptoms or your partner has tested positive, you may be started on the treatment before you get your results.
Chlamydia antibiotic treatments
Treatment for chlamydia is relatively simple, involving a short course of antibiotic tablets. The two most prescribed antibiotics for chlamydia are doxycycline, which is the most effective treatment, and azithromycin which is an effective alternative for people who cannot tolerate doxycycline.
Doxycycline
Doxycycline is taken twice a day for one week. It usually starts working around 48 hours after being taken, however you should avoid any form of sexual contact for 7 days after you have finished treatment because it can take this length of time for your body to be free from chlamydia.
It is important to complete the course to ensure that the bacteria causing the infection has been killed and has no chance of multiplying.
The medical questionnaire will determine whether doxycycline is suitable for you to take or not.
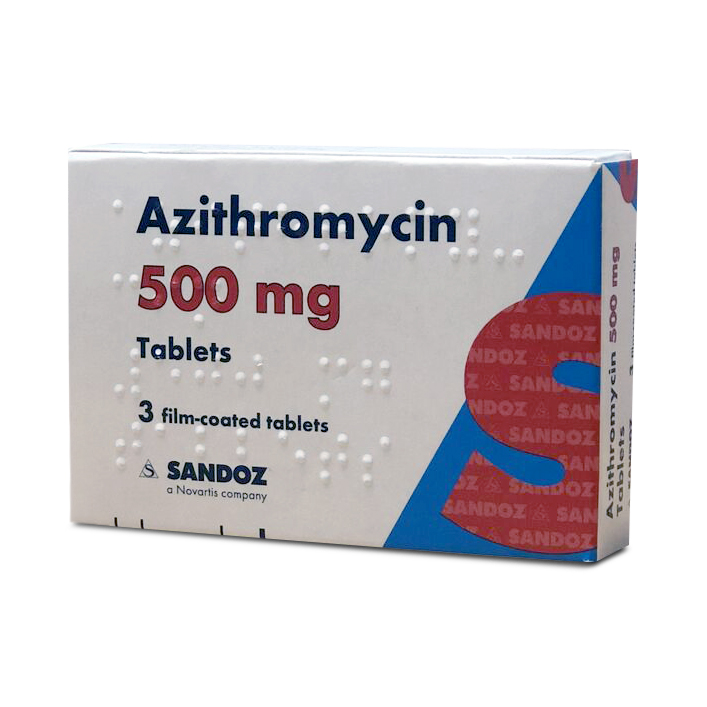
Azithromycin
Azithromycin is taken daily for three days. It starts to work immediately, but the infection can take 7 days after the course has been completed to be cleared. Although azithromycin is the fastest way to get rid of chlamydia, it is the second line treatment and should only be used where doxycycline cannot be taken. This is because extensive use of this antibiotic has led to the development of resistance in the infection.
How do chlamydia tablets work?
Chlamydia tablets work by stopping the bacteria's production of proteins, which they require to survive and replicate. As the antibiotics kill the bacteria, symptoms of chlamydia usually start to improve.
How long does it take for treatment to work?
Doxycycline starts working in around 48 hours and azithromycin starts to work immediately.
How effective is chlamydia treatment?
Research suggests that when taken correctly doxycycline has a 100% success rate in treating chlamydia, while clinical studies have proven a 97% success rate with azithromycin.
What are the side effects of chlamydia treatment?
Chlamydia tablets are usually well tolerated, however, as with all medication, side effects may be present. Side effects are usually mild, and most people will not experience them. Common side effects of chlamydia treatment include:
- Stomach pain
- Diarrhoea
- Sickness
- Thrush
Does chlamydia go away on its own without treatment?
No, it typically does not go away on its own. If you do not get treatment, the infection can persist and lead to complications. Untreated chlamydia can cause damage to the reproductive system, leading to issues such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility and ectopic pregnancy in women, and epididymitis and infertility in men.
How long will I test positive for chlamydia after a treatment course?
You can test positive for up to 6 weeks after completing your antibiotics. If you still test positive after 6 weeks, treatment was not successful
How to prevent chlamydia
Chlamydia is transmitted through having unprotected sex, therefore using a condom every time you have vaginal or anal sex will help to prevent the spread of chlamydia.
During oral sex or when rubbing female genitals together, you should use a dam to cover the female genitals or a condom to cover the penis. Avoid sharing sex toys, however if you do, make sure toys are washed or cover them with a new condom between each person who uses them.
Sources
-
NHS UK. (n.d.). Chlamydia. Retrieved May 3, 2024, from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/chlamydia/
-
British Association for Sexual Health and HIV. (2015). Chlamydia: 2015 UK National Guideline for the Management of Infection with Chlamydia trachomatis (2015). Retrieved May 3, 2024, from https://www.bashh.org/resources/15/chlamydia_2015/
-
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. (n.d.). Chlamydia - Uncomplicated Genital. Retrieved May 3, 2024, from https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/chlamydia-uncomplicated-genital/
No, chlamydia tablets are not available over the counter. This is because they contain antibiotics and require a consultation with a doctor or pharmacist.
Antibiotics for chlamydia are highly effective, and most of the time, chlamydia goes away. Unlike herpes, chlamydia does not stay in your system for life. However, chlamydia can come back after treatment if you contract the infection again. Antibiotics do not provide protection going forward and will only treat current infections. You should take adequate precautionary measures to protect yourself. We recommend carrying out a chlamydia test each time you have a new sexual partner.
No, you cannot get chlamydia from kissing. Chlamydia is transmitted through the exchange of bodily fluids during sexual activities, particularly through contact with infected genital secretions.
Yes, chlamydia can be spread through oral sex. Performing oral sex on an infected person can lead to throat chlamydia.
Although transmission is not guaranteed, if your partner has chlamydia, it can significantly increase your risk of contracting it, especially if you have unprotected sexual contact. It is important that both you and your partner get tested if you think chlamydia is present so can get treated as soon as possible.
Yes, antibiotic tablets will only work to cure a current infection. They will not provide protection from future infections you may contract.
Azithromycin is the safest option for pregnant women who have chlamydia. It is important to get treated before birth, to avoid passing the infection on to your child. It is possible for the child to develop an eye or chest infection if the mother has chlamydia.
Pregnant women should not take doxycycline, as this can affect the development of the baby’s teeth and bones. Unfortunately, we are unable to provide treatment to pregnant women. You should visit your local GUM clinic or see your GP as soon as possible.